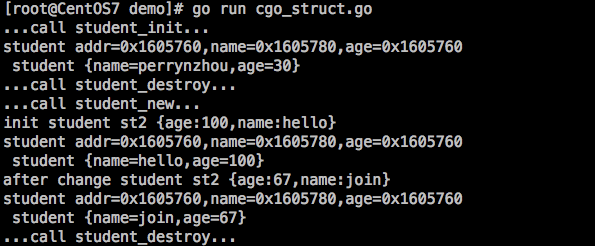
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
| // go run cgo.go
package main
/*
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef struct student {
int age;
char *name;
}student;
void student_init(void **ptr,char *name,int age) {
size_t len = strlen(name);
student *st = (student *)calloc(1,sizeof(student));
assert(st!=NULL);
st->age = age;
st->name = (char *)calloc(1,len+1);
memcpy(st->name,name,len);
*ptr = st;
fprintf(stdout,"...call student_init...\n");
}
student *student_new(char *name,int age) {
size_t len = strlen(name);
student *st = (student *)calloc(1,sizeof(student));
assert(st!=NULL);
st->age = age;
st->name = (char *)calloc(1,len+1);
memcpy(st->name,name,len);
fprintf(stdout,"...call student_new...\n");
return st;
}
void student_destroy(void *ptr) {
student *st = (student *)ptr;
if(st !=NULL)
{
free(st->name);
free(st);
st=NULL;
fprintf(stdout,"...call student_destroy...\n");
}
}
void student_print(void *ptr) {
student *st = (student *)ptr;
fprintf(stdout,"student addr=%p,name=%p,age=%p\n",st,st->name,&st->age);
fprintf(stdout," student {name=%s,age=%d}\n",st->name,st->age);
}
*/
import "C"
import (
"fmt"
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
var st1 unsafe.Pointer
name := C.CString("perrynzhou")
C.student_init(&st1, name, 30)
C.student_print(st1)
C.student_destroy(st1)
C.free(unsafe.Pointer(name))
var st2 *C.student
name2 := C.CString("hello")
st2 = C.student_new(name2, 100)
fmt.Printf("init student st2 {age:%d,name:%s}\n", st2.age, C.GoString(st2.name))
C.student_print(unsafe.Pointer(st2))
C.free(unsafe.Pointer(st2.name))
name3 := C.CString("join")
st2.name = name3
st2.age = 67
fmt.Printf("after change student st2 {age:%d,name:%s}\n", st2.age, C.GoString(st2.name))
C.student_print(unsafe.Pointer(st2))
C.student_destroy(unsafe.Pointer(st2))
}
|