1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
| #include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define FILE_NAME "/tmp/out"
static void redirect_stdout_without_dup() {
fprintf(stdout, "pid=%d\n", getpid());
const char *str = "my dup\n";
//关闭 stdout
close(1);
//当前process中描述符表中最小可用的下标是1,因为刚刚关闭
int fd = open(FILE_NAME, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0666);
if (fd > 0) {
// stdout 在每个进程描述表中的下标为1
//此时,数据是写到了刚刚打开的fd中,新打开的fd返回的是1
fprintf(stdout, " open fd=%d\n", fd);
// write 操作也是写到fd=1中,当前进程中文件描述符为1的并不是标准输出
write(fd, str, strlen(str));
close(1);
}
}
static void redirect_stdout_with_dup() {
fprintf(stdout, "pid=%d\n", getpid());
const char *str = "my dup";
//默认打开fd,在当前进程描述表中fd并不是{0,1,2}
int fd = open(FILE_NAME, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0666);
if (fd > 0) {
//关闭标准的输出的文件描述符
close(1);
//拷贝fd到当前进程描述符中最小的下标位置,当前最小的下标应该是刚刚关闭的1
dup(fd);
// fprintf的内容写入到了fd中,并没有写入到标准输出中
fprintf(stdout, " open fd=%d\n", fd);
write(fd, str, strlen(str));
//关闭当前文件描述符
close(fd);
}
}
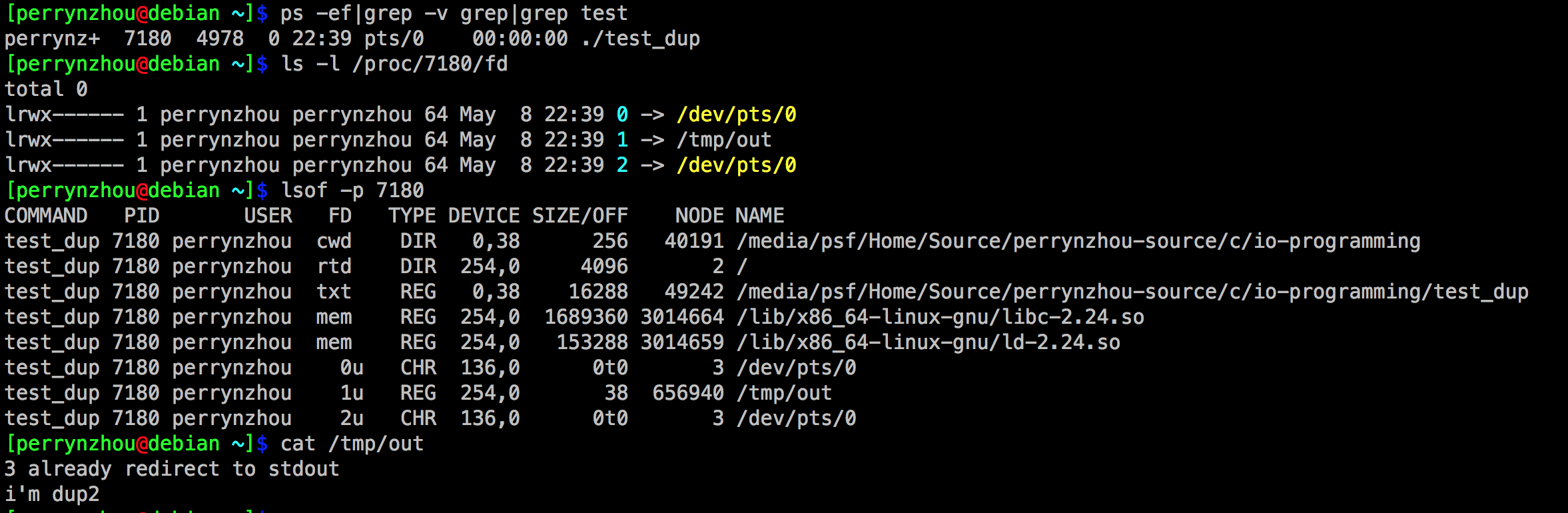
static void redirect_stdout_with_dup2() {
fprintf(stdout, "pid=%d\n", getpid());
const char *str = "i'm dup2\n";
//打开一个新的文件描述符
int fd = open(FILE_NAME, O_RDWR | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0666);
if (fd > 0) {
//如果1号文件描述符是打开状态,就关闭1号文件描述符
//把当前进程中文件描述符表中下标为fd的指针拷贝下标为1的空间
//如果fd==1就直接返回fd
dup2(fd, 1); // equals: close(1) and dup(fd)
// fd和1号文件描述符指向相同的文件结构体指针
fprintf(stdout, "%d already redirect to stdout\n", fd);
write(fd, str, strlen(str));
//刷盘操作
if (fd != 1) {
close(fd);
}
}
}
int main(void) {
/*
redirect_stdout_without_dup();
redirect_stdout_with_dup();
*/
redirect_stdout_with_dup2();
for (;;) {
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
|